namespace std {
template <class OuterAlloc, class... InnerAllocs>
class scoped_allocator_adaptor : public OuterAlloc;
}
概要
scoped_allocator_adaptorは、vector<string>のように、メモリ確保を行う型が入れ子になっているような場合に、外側と内側でアロケータオブジェクトを共有するための、アロケータクラスのアダプタである。
以下は、このアダプタクラスを使用することによって変化する、コンテナのメモリイメージである。
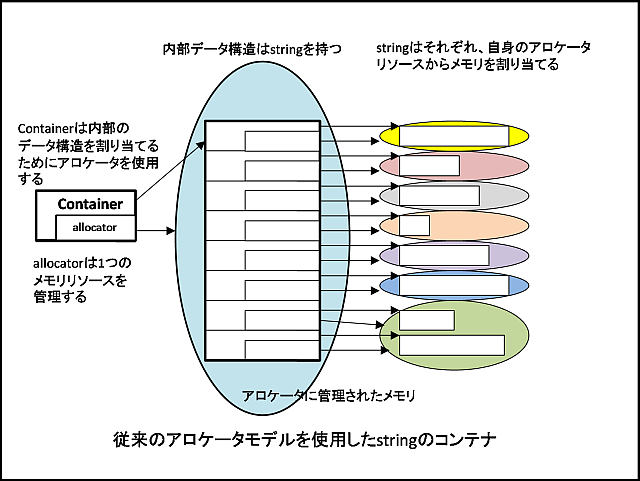
図1 コンテナ、および各要素がそれぞれに別個のアロケータオブジェクトを持つ
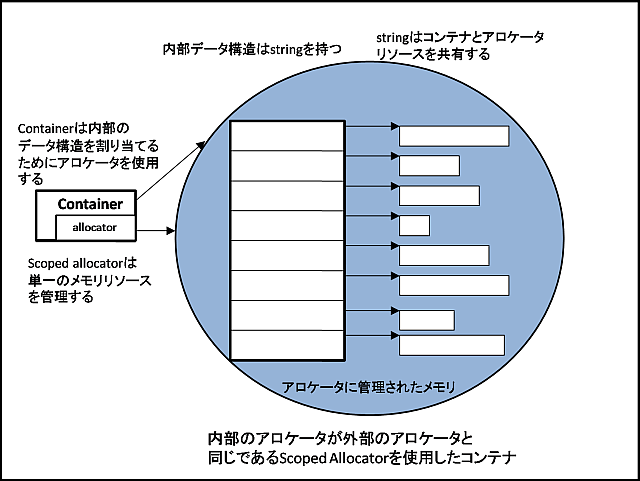
図2 コンテナとその要素で、アロケータオブジェクトの状態を伝播させる(例1)
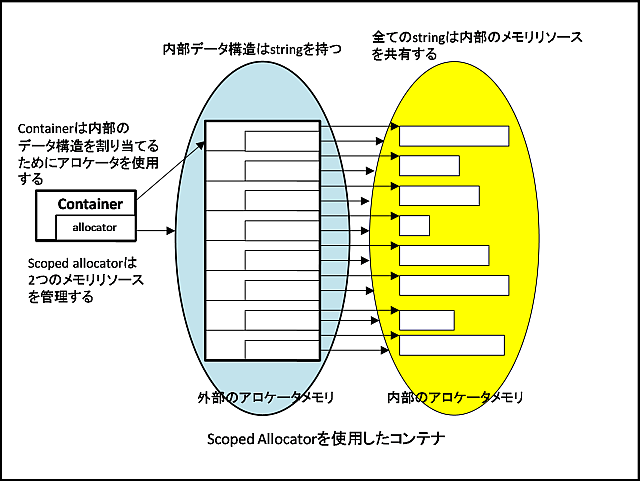
図3 全ての要素にアロケータオブジェクトの状態を伝播させる(例2)
テンプレートパラメータは、以下を意味する:
OuterAlloc: 外側のアロケータ。(たとえばコンテナのアロケータ)InnerAlloc...: 内側のアロケータ。(たとえばコンテナの要素に対するアロケータ)
メンバ関数
| 名前 | 説明 | 対応バージョン |
|---|---|---|
(constructor) |
コンストラクタ | C++11 |
~scoped_allocator_adaptor() = default |
デストラクタ | C++11 |
inner_allocator |
内側のアロケータを取得する | C++11 |
outer_allocator |
外側のアロケータを取得する | C++11 |
allocate |
メモリを確保する | C++11 |
deallocate |
メモリを解放する | C++11 |
max_size |
一度に確保可能なメモリの最大サイズを取得する | C++11 |
construct |
オブジェクトを構築する | C++11 |
destroy |
オブジェクトを破棄する | C++11 |
select_on_container_copy_construction |
コンテナのコピー構築に必要なアロケータを取得する | C++11 |
メンバ型
| 名前 | 説明 | 対応バージョン |
|---|---|---|
outer_allocator_type |
外側のアロケータOuterAlloc |
C++11 |
inner_allocator_type |
内側のアロケータ。 InnerAllocsが空だったらscoped_allocator_adaptor<OuterAlloc>。空じゃなければscoped_allocator_adaptor<InnerAllocs...>。 |
C++11 |
value_type |
要素型allocator_traits<OuterAlloc>::value_type |
C++11 |
size_type |
要素数を表す符号なし整数型 allocator_traits<OuterAlloc>::size_type |
C++11 |
difference_type |
ポインタの差を表す符号付き整数型allocator_traits<OuterAlloc>::difference_type |
C++11 |
pointer |
要素のポインタ型allocator_traits<OuterAlloc>::pointer |
C++11 |
const_pointer |
読み取り専用の要素のポインタ型 allocator_traits<OuterAlloc>::const_pointer |
C++11 |
void_pointer |
voidポインタ型 allocator_traits<OuterAlloc>::void_pointer |
C++11 |
const_void_pointer |
読み取り専用のvoidポインタ型 allocator_traits<OuterAlloc>::const_void_pointer |
C++11 |
propagate_on_container_copy_assignment |
コンテナのコピー代入でアロケータを置き換えるかどうかを示す論理型。OuterAlloc::propagate_on_container_copy_assignmentが存在する場合はその型が使用され、そうでなければfalse_typeが使用される。 |
C++11 |
propagate_on_container_move_assignment |
コンテナのムーブ代入でアロケータを置き換えるかどうかを示す論理型。OuterAlloc::propagate_on_container_move_assignmentが存在する場合はその型が使用され、そうでなければfalse_typeが使用される。 |
C++11 |
propagate_on_container_swap |
コンテナのswap操作でアロケータを置き換えるかどうかを示す論理型。OuterAlloc::propagate_on_container_swapが存在する場合はその型が使用され、そうでなければfalse_typeが使用される。 |
C++11 |
is_always_equal |
OuterAlloc および InnerAlloc... のすべてのアロケータ A について std::allocator_traits<A>::is_always_equal::value が true であれば std::true_type。そうでなければstd::false_type。 |
C++17 |
rebind<U> |
型Uを確保するように再束縛する |
C++11 |
非メンバ関数
| 名前 | 説明 | 対応バージョン |
|---|---|---|
operator== |
等値比較 | C++11 |
operator!= |
非等値比較 | C++11 |
推論補助
| 名前 | 説明 | 対応バージョン |
|---|---|---|
(deduction_guide) |
クラステンプレートの推論補助 | C++17 |
例1 コンテナとその要素で、アロケータオブジェクトの状態を伝播させる
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <forward_list>
#include <scoped_allocator>
// std::allocatorに状態変数を持たせただけのクラス
template <class T>
class MyAlloc : public std::allocator<T> {
int state_; // 状態
template <class> friend class MyAlloc;
public:
template <class U>
struct rebind { using other = MyAlloc<U>; };
MyAlloc(int state = 0)
: state_(state) {}
template <class U>
MyAlloc(const MyAlloc<U>& alloc)
: state_(alloc.state_) {}
int getState() const { return state_; }
};
template <class T, class U>
bool operator==(const MyAlloc<T>& lhs, const MyAlloc<U>& rhs)
{ return lhs.getState() == rhs.getState(); }
template <class T, class U>
bool operator!=(const MyAlloc<T>& lhs, const MyAlloc<U>& rhs)
{ return lhs.getState() != rhs.getState(); }
// コンテナの要素(Inner)
using forward_list = std::forward_list<
int,
MyAlloc<int>
>;
// コンテナ(Outer)
template <class T>
using vector = std::vector<
T,
std::scoped_allocator_adaptor<MyAlloc<T>>
>;
int main()
{
// stringで使用するアロケータオブジェクトを、
// vectorでも使用する
int state = 5;
MyAlloc<forward_list> alloc(state);
vector<forward_list> v(alloc);
v.push_back(forward_list{100});
v.push_back(forward_list{200});
// 同じアロケータオブジェクトが使われていることを確認する。
// getState()の値が、どちらも5になる。
std::cout << v.get_allocator().getState() << std::endl;
std::cout << v.front().get_allocator().getState() << std::endl;
}
出力
5
5
例2 全ての要素にアロケータオブジェクトの状態を伝播させる
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <forward_list>
#include <scoped_allocator>
// std::allocatorに状態変数を持たせただけのクラス
template <class T>
class MyAlloc : public std::allocator<T> {
int state_; // 状態
template <class> friend class MyAlloc;
public:
template <class U>
struct rebind { using other = MyAlloc<U>; };
MyAlloc(int state = 0)
: state_(state) {}
template <class U>
MyAlloc(const MyAlloc<U>& alloc)
: state_(alloc.state_) {}
int getState() const { return state_; }
};
template <class T, class U>
bool operator==(const MyAlloc<T>& lhs, const MyAlloc<U>& rhs)
{ return lhs.getState() == rhs.getState(); }
template <class T, class U>
bool operator!=(const MyAlloc<T>& lhs, const MyAlloc<U>& rhs)
{ return lhs.getState() != rhs.getState(); }
// コンテナの要素(Inner)
using forward_list = std::forward_list<
int,
MyAlloc<int>
>;
// コンテナ(Outer)
template <class T>
using vector = std::vector<
T,
std::scoped_allocator_adaptor<MyAlloc<T>, MyAlloc<typename T::value_type>>
>;
int main()
{
int outer_state = 5;
int inner_state = 2;
vector<forward_list>::allocator_type alloc {
(MyAlloc<forward_list>(outer_state)), // vector自体のアロケータオブジェクト
(MyAlloc<int>(inner_state)) // vectorの全ての要素に使用するアロケータオブジェクト
};
vector<forward_list> v(alloc);
v.push_back(forward_list{100});
v.push_back(forward_list{200});
// コンテナに使用されるアロケータの状態を確認
// 5になる(outer_state)
std::cout << "container allocator : " << v.get_allocator().getState() << std::endl;
// 要素に使用されるアロケータの状態を確認
// 全ての要素に、アロケータの状態が伝播される
for (const forward_list& x : v) {
std::cout << "element allocator : " << x.get_allocator().getState() << std::endl;
}
}
出力
container allocator : 5
element allocator : 2
element allocator : 2
バージョン
言語
- C++11
処理系
- Clang: 3.0 ✅, 3.1 ✅, 3.2 ✅, 3.3 ✅, 3.4 ✅, 3.5 ✅, 3.6 ✅
- GCC: 4.7.3 ✅, 4.8.1 ✅, 4.8.2 ✅, 4.9.0 ✅, 4.9.1 ✅, 5.0.0 ✅
- ICC: ??
- Visual C++: ??