namespace std {
float atan2(float y, float x); // (1) C++03からC++20まで
double atan2(double y, double x); // (2) C++03からC++20まで
long double
atan2(long double y, long double x); // (3) C++03からC++20まで
floating-point-type
atan2(floating-point-type y,
floating-point-type x); // (4) C++23
constexpr floating-point-type
atan2(floating-point-type y,
floating-point-type x); // (4) C++26
Promoted
atan2(Arithmetic1 y,
Arithmetic2 x); // (5) C++11
constexpr Promoted
atan2(Arithmetic1 y,
Arithmetic2 x); // (5) C++26
float
atan2f(float y, float x); // (6) C++17
constexpr float
atan2f(float y, float x); // (6) C++26
long double
atan2l(long double y, long double x); // (7) C++17
constexpr long double
atan2l(long double y, long double x); // (7) C++26
}
概要
算術型の逆正接(アークタンジェント)を対辺と隣辺から求める。
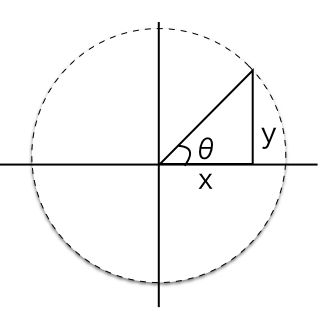
このような三角形があった場合、辺yの長さと辺xの長さをatan2()関数に与えることで、角度θがラジアン単位として求まる。
- (1) :
floatに対するオーバーロード - (2) :
doubleに対するオーバーロード - (3) :
long doubleに対するオーバーロード - (4) : 浮動小数点数型に対するオーバーロード
- (5) : 算術型に対するオーバーロード (大きい精度にキャストして計算される。整数は
doubleで計算される) - (6) :
float型規定 - (7) :
long double型規定
戻り値
y / x の逆正接を [-π, π] の範囲で返す。(単位はラジアン)
象限は引数の符号から適切に求められる。
yとxの両方が値0である場合に定義域エラーとなる可能性がある。定義域エラーが発生した場合、戻り値は処理系定義である。(備考参照)
備考
-
$$ f(y, x) = \mathrm{Arctan}~\frac{y}{x} $$
引数の順番に注意されたし。
-
定義域エラーが発生した場合の挙動については、
<cmath>を参照。 -
C++11 以降では、処理系が IEC 60559 に準拠している場合(
std::numeric_limits<T>::is_iec559() != false)、以下の規定が追加される。(複号同順)y = ±0でx < 0またはx = -0の場合、戻り値は±πとなる。y = ±0でx > 0またはx = +0の場合、戻り値は±0となる。y > 0でx = ±0の場合、戻り値は+π/2となる。y < 0でx = ±0の場合、戻り値は-π/2となる。0 < z < +∞とすると、y = ±zでx = -∞の場合、戻り値は±πとなる。0 < z < +∞とすると、y = ±zでx = +∞の場合、戻り値は±0となる。y = ±∞でxが有限の値の場合、戻り値は±π/2となる。y = ±∞でx = -∞の場合、戻り値は±3π/4となる。y = ±∞でx = +∞の場合、戻り値は±π/4となる。
特に、
yとxの両方がゼロの場合に定義域エラー(FE_INVALID(無効演算浮動小数点例外))となったり、yが非ゼロでxがゼロの場合に極エラー(FE_DIVBYZERO(ゼロ除算浮動小数点例外))となったりはしない事に注意。 -
C++23では、(1), (2), (3)が(4)に統合され、拡張浮動小数点数型を含む浮動小数点数型へのオーバーロードとして定義された
例
#include <cmath>
#include <iostream>
int main() {
std::cout << std::fixed;
std::cout << "atan2(0.0, 1.0) = " << std::atan2(0.0, 1.0) << std::endl;
std::cout << "atan2(1.0, 1.0) = " << std::atan2(1.0, 1.0) << std::endl;
std::cout << "atan2(1.0, 0.0) = " << std::atan2(1.0, 0.0) << std::endl;
std::cout << "atan2(1.0, -1.0) = " << std::atan2(1.0, -1.0) << std::endl;
std::cout << "atan2(0.0, -1.0) = " << std::atan2(0.0, -1.0) << std::endl;
std::cout << "atan2(-1.0, -1.0) = " << std::atan2(-1.0, -1.0) << std::endl;
std::cout << "atan2(-1.0, 0.0) = " << std::atan2(-1.0, 0.0) << std::endl;
std::cout << "atan2(-1.0, 1.0) = " << std::atan2(-1.0, 1.0) << std::endl;
}
出力
atan2(0.0, 1.0) = 0.000000
atan2(1.0, 1.0) = 0.785398
atan2(1.0, 0.0) = 1.570796
atan2(1.0, -1.0) = 2.356194
atan2(0.0, -1.0) = 3.141593
atan2(-1.0, -1.0) = -2.356194
atan2(-1.0, 0.0) = -1.570796
atan2(-1.0, 1.0) = -0.785398
バージョン
言語
- C++03
処理系
- Clang: 1.9 ✅, 2.9 ✅, 3.1 ✅
- GCC: 3.4.6 ✅, 4.2.4 ✅, 4.3.5 ✅, 4.4.5 ✅, 4.5.1 ✅, 4.5.2 ✅, 4.6.1 ✅, 4.7.0 ✅
- ICC: 10.1 ✅, 11.0 ✅, 11.1 ✅, 12.0 ✅
- Visual C++: 2003 ✅, 2005 ✅, 2008 ✅, 2010 ✅
備考
特定の環境では、早期に constexpr 対応されている場合がある:
- GCC 4.6.1 以上
実装例
[-π/2, π/2] の範囲を返す atan があれば、引数の符号に応じて以下のように変換することで求められる。
$$ \mathrm{Arctan}~\frac{y}{x} = \begin{cases} \displaystyle \mathrm{Arctan}~\frac{y}{x} & \quad \mathrm{for} \; 0 \le x \\[2ex] \displaystyle \mathrm{Arctan}~\frac{y}{x} + \pi & \quad \mathrm{for} \; x < 0, \; 0 \le y \\[2ex] \displaystyle \mathrm{Arctan}~\frac{y}{x} - \pi & \quad \mathrm{for} \; x < 0, \; y < 0 \end{cases} $$