namespace std {
float sin(float x); // (1) C++03からC++20まで
double sin(double x); // (2) C++03からC++20まで
long double sin(long double x); // (3) C++03からC++20まで
floating-point-type
sin(floating-point-type x); // (4) C++23
constexpr floating-point-type
sin(floating-point-type x); // (4) C++26
double
sin(Integral x); // (5) C++11
constexpr double
sin(Integral x); // (5) C++26
float
sinf(float x); // (6) C++17
constexpr float
sinf(float x); // (6) C++26
long double
sinl(long double x); // (7) C++17
constexpr long double
sinl(long double x); // (7) C++26
}
概要
算術型の正弦(サイン)を求める。
- (1) :
floatに対するオーバーロード - (2) :
doubleに対するオーバーロード - (3) :
long doubleに対するオーバーロード - (4) : 浮動小数点数型に対するオーバーロード
- (5) : 整数型に対するオーバーロード (
doubleにキャストして計算される) - (6) :
float型規定 - (7) :
long double型規定
戻り値
引数 x の正弦を返す(xの単位はラジアン)。
備考
- $$ f(x) = \sin x $$
- C++11 以降では、処理系が IEC 60559 に準拠している場合(
std::numeric_limits<T>::is_iec559() != false)、以下の規定が追加される。x = ±0の場合、戻り値は±0となる。(複号同順)x = ±∞の場合、戻り値は quiet NaN となり、FE_INVALID(無効演算浮動小数点例外)が発生する。
- C++23では、(1), (2), (3)が(4)に統合され、拡張浮動小数点数型を含む浮動小数点数型へのオーバーロードとして定義された
例
基本的な使い方
#include <cmath>
#include <iostream>
int main() {
static const double pi = 3.141592653589793;
std::cout << std::fixed;
std::cout << "sin(0.0) = " << std::sin(0.0) << std::endl;
std::cout << "sin(pi/6) = " << std::sin(pi/6) << std::endl;
std::cout << "sin(pi/4) = " << std::sin(pi/4) << std::endl;
std::cout << "sin(pi/3) = " << std::sin(pi/3) << std::endl;
std::cout << "sin(pi/2) = " << std::sin(pi/2) << std::endl;
std::cout << "sin(pi) = " << std::sin(pi) << std::endl;
}
出力例
sin(0.0) = 0.000000
sin(pi/6) = 0.500000
sin(pi/4) = 0.707107
sin(pi/3) = 0.866025
sin(pi/2) = 1.000000
sin(pi) = 0.000000
値の遷移
この例で得られた値の遷移は、以下の図のようになる:
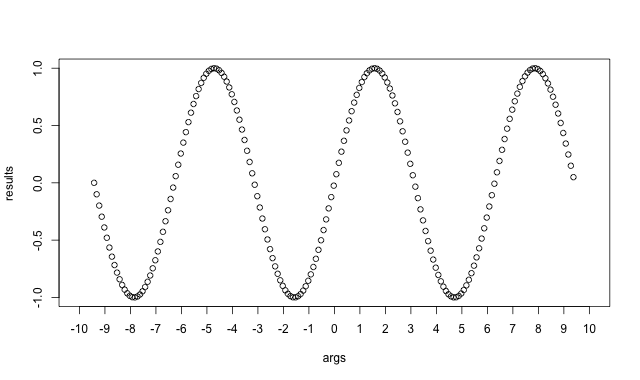
このような値の遷移は、正弦波, サインカーブとして知られている。
バージョン
言語
- C++03
処理系
- Clang: 1.9 ✅, 2.9 ✅, 3.1 ✅
- GCC: 3.4.6 ✅, 4.2.4 ✅, 4.3.5 ✅, 4.4.5 ✅, 4.5.1 ✅, 4.5.2 ✅, 4.6.1 ✅, 4.7.0 ✅
- ICC: 10.1 ✅, 11.0 ✅, 11.1 ✅, 12.0 ✅
- Visual C++: 2003 ✅, 2005 ✅, 2008 ✅, 2010 ✅
備考
特定の環境では、早期に constexpr 対応されている場合がある:
- GCC 4.6.1 以上
実装例
以下のマクローリン級数を適当な次数で打ち切ることで近似的に求めることができる。
$$ \sin x = \sum_{n = 0}^{\infty} \frac{(-1)^n}{(2n + 1)!} x^{2n + 1} \quad \mathrm{for~all} \; x $$